
Last updated: June 2024 / 849719 o'block
Partially signed Bitcoin transactions (PSBTs) are enabled by a Bitcoin standard that improves the interoperability between wallets by making it easier to communicate and sign unsigned transactions. It facilitates more complex transactions such as multisig and CoinJoin. (That's where the 'partially signed' part comes from: where there are multiple parties signing the same transaction, they each sign it partially before it's assembled into a fully signed transaction.)
It also enables easier air-gapped cold storage. Whereas for most users just a Bitcoin hardware wallet used on your regular online computer will do the job (as hardware wallets have an offline secure element built-in), if you don't have a hardware wallet at hand or want to make extra-sure by keeping it air-gapped, the PSBT standard makes it easier to sign a transaction offline from a cold wallet and then transmit it to the network through a device connected to the Internet.
Here's an example of what that looks like in practice.
Creating two wallets:
- one is air-gapped, on a device with no direct connection to the Internet to help ensure the private key it stores is secure
- the wallet is on a device that is connected to the Internet, and it is a
watch-only,
meaning it is created from a public key and can't reveal the private key even if the device is infected with malware.
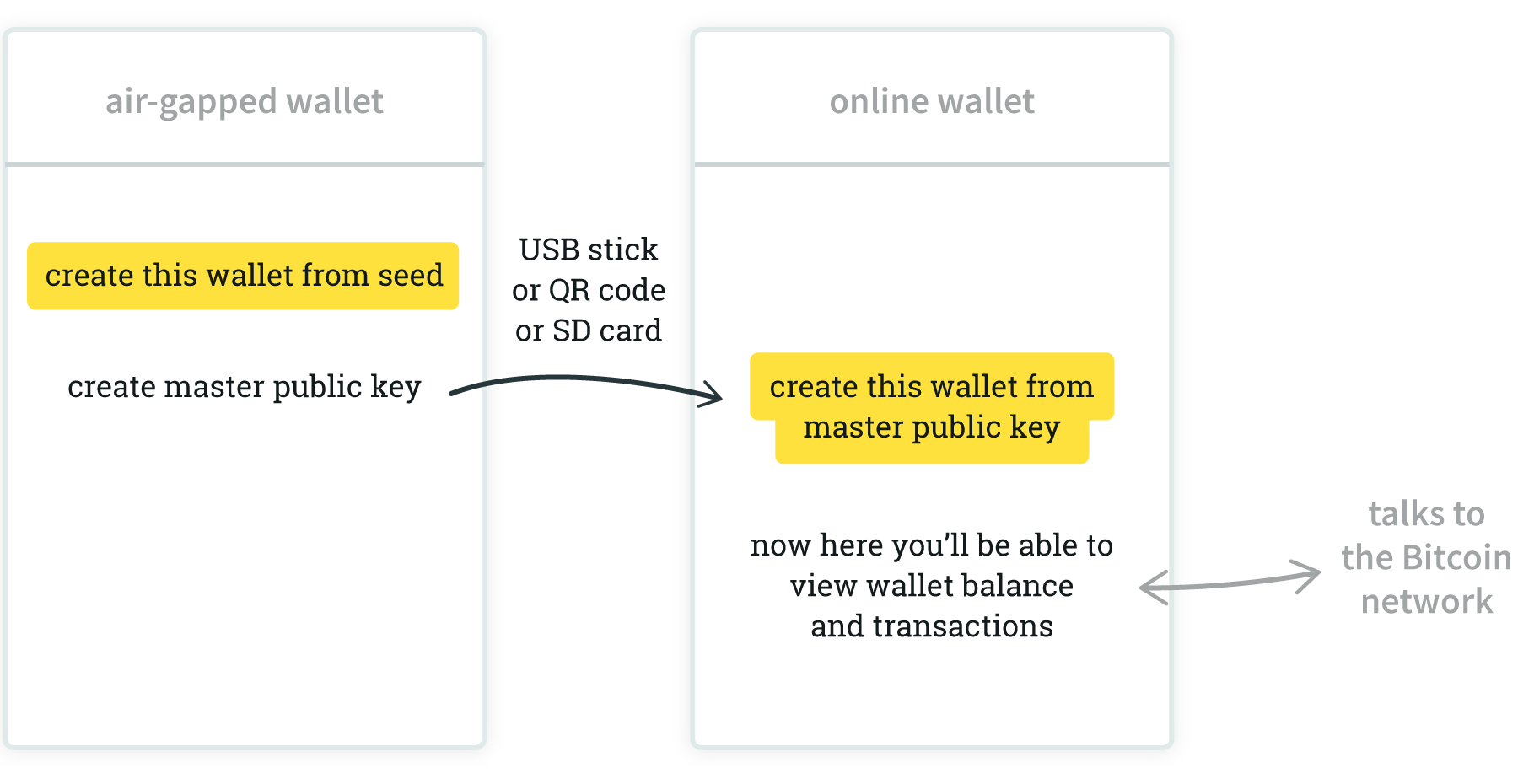
Information between the devices is carried by an SD card, QR code or a USB stick. (If using a USB stick, monitor it for data being written to it as it can carry any kind of data, including malware.)
Note that your seed/private keys are never entered into the online wallet. They are kept secure on the air-gapped device.
Your offline wallet, because it has no Internet access, won't be able to receive information from the Bitcoin network about your bitcoin balance. But your online wallet has Internet access and has your transactions and your balance.
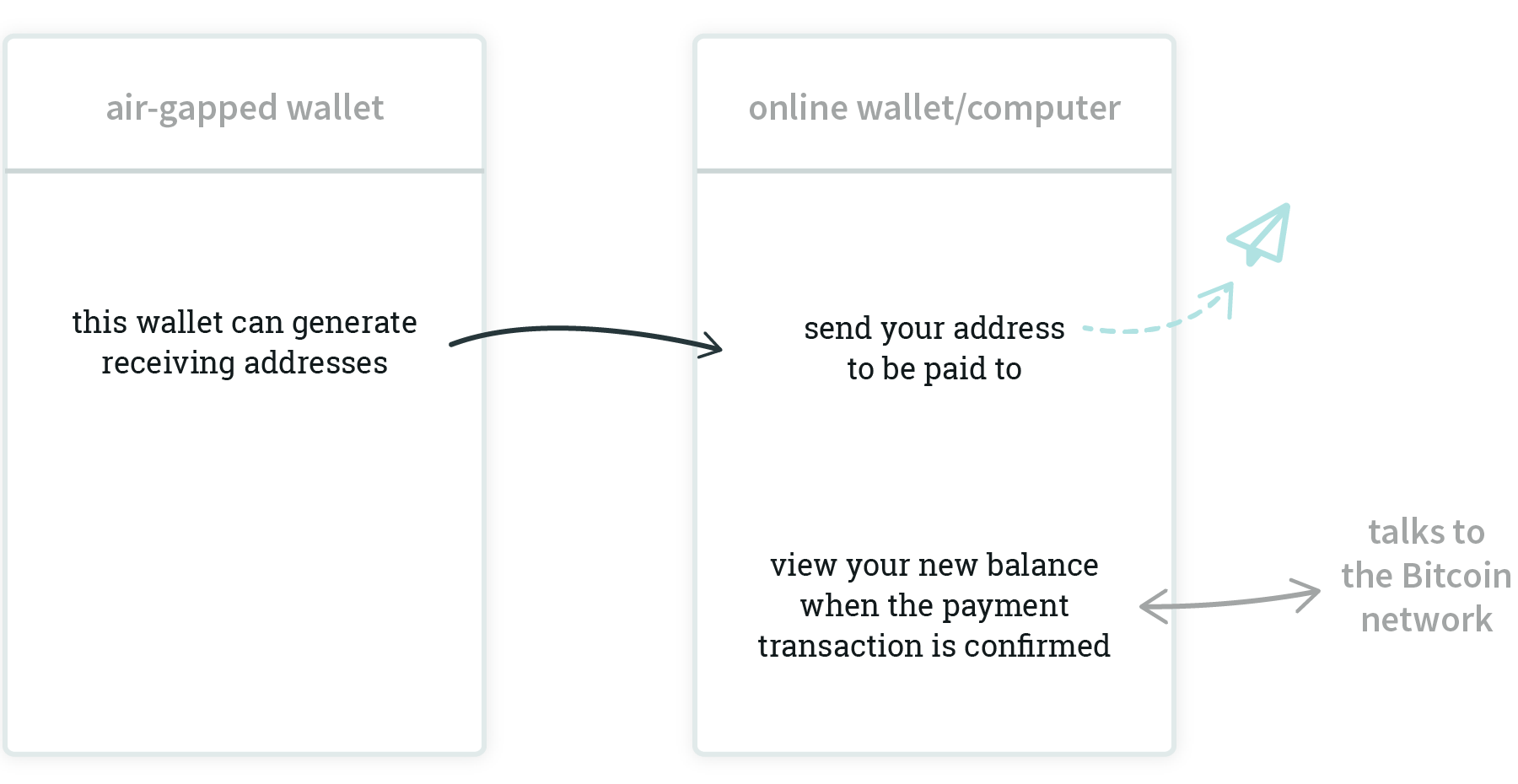
Receiving bitcoin with this setup is not much different from using any other kind of wallet, except if you generate the receiving address on the air-gapped device, you have to move it to the online device to be able to send the address to the person sending you bitcoin. (If this is confusing - yes, you absolutely can generate a receiving address on a wallet without a connection to the Internet and the Bitcoin network.)
The watch-only wallet on a device that's online starts the process by creating a PSBT. Think of it as a cheque that needs to be signed.
The transaction info is then transferred to the offline device so that the cold wallet which does have the private keys can sign it.
The signed transaction is moved back to the online wallet so it can broadcast it to the Bitcoin network where it'll be validated and mined.
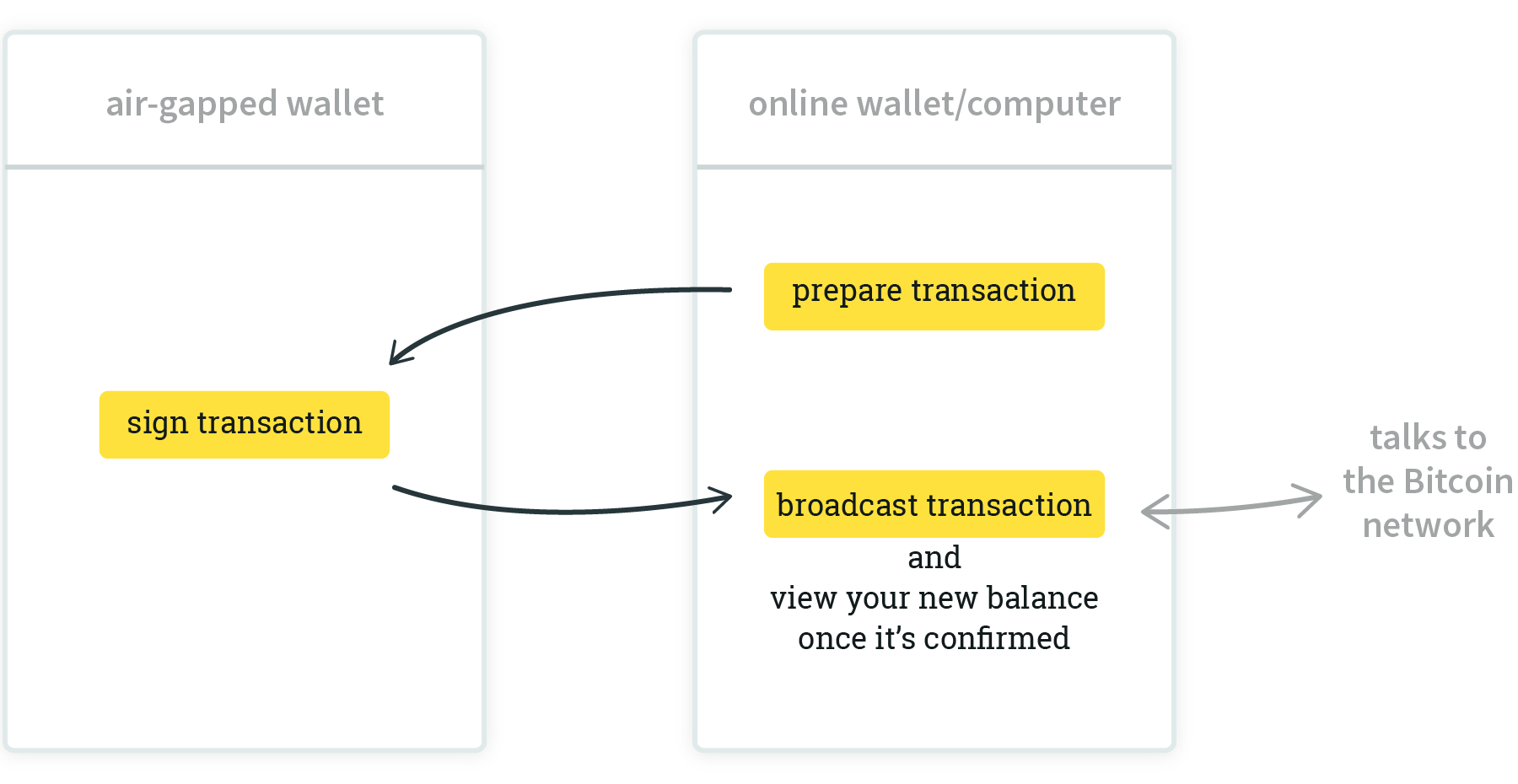
Note that your seed/private keys remain safe on the air-gapped device, and only the signed transaction is moved to the online device.
***
The PSBT standard is adopted by wallets like Bitcoin Core, Electrum, BlueWallet, and Sparrow.
Graphical abstract: for when you just need a quick overview or reminder - same stuff as above, just all in one image.